Application Dependencies
Application dependencies are the libraries other than your project code that are required to create and run your application.
Why are application dependencies important?
Python web applications are built upon the work done by thousands of open source programmers. Application dependencies include not only web frameworks but also libraries for scraping, parsing, processing, analyzing, visualizing, and many other tasks. Python's ecosystem facilitates discovery, retrieval and installation so applications are easier for developers to create.
Finding libraries
Python libraries are stored in a central location known as the Python Package Index (PyPi). PyPi contains search functionality with results weighted by usage and relevance based on keyword terms.
Besides PyPi there are numerous resources that list common or "must-have" libraries. Ultimately the decision for which application dependencies are necessary for your project is up to you and the functionality you're looking to build. However, it's useful to browse through these lists in case you come across a library to solve a problem by reusing the code instead of writing it all yourself. A few of the best collections of Python libraries are
-
Python.org's useful modules which groups modules into categories.
-
GitHub Explore Trending repositories shows the open source Python projects trending today, this week, and this month.
-
This list of 20 Python libraries you can’t live without is a wide-ranging collection from data analysis to testing tools.
-
Wikipedia actually has an extensive page dedicated to Python libraries grouped by categories.
Isolating dependencies
Dependencies are installed separately from system-level packages to prevent library version conflicts. The most common isolation method is virtualenv. Each virtualenv is its own copy of the Python interpreter and dependencies in the site-packages directory. To use a virtualenv it must first be created with the virtualenv command and then activated.
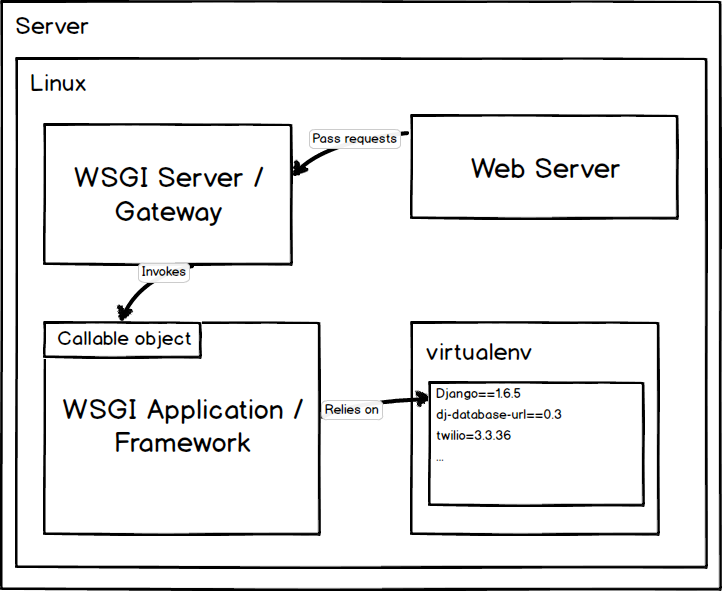
The virtualenv stores dependencies in an isolated environment. The web application then relies only on that virtualenv instance which has a separate copy of the Python interpreter and site-packages directory. A high level of how a server configured with virtualenv can look is shown in the picture below.
Installing Python dependencies
The recommended way to install Python library dependencies is with the pip command when a virtualenv is activated.
Pip and virtualenv work together and have complementary responsibilities. Pip downloads and installs application dependencies from the central PyPi repository.
requirements.txt
The pip convention for specifying application dependencies is with a
requirements.txt file. When you build a Python web application you
should include requirements.txt in the base directory of your project.
Python projects' dependencies for a web application should be specified with pegged dependencies like the following:
django==1.6
bpython==0.12
django-braces==0.2.1
django-model-utils==1.1.0
logutils==0.3.3
South==0.7.6
requests==1.2.0
stripe==1.9.1
dj-database-url==0.2.1
django-oauth2-provider==0.2.4
djangorestframework==2.3.1
Pegged dependencies with precise version numbers or Git tags are important because otherwise the latest version of a dependency will be used. While it may sound good to stay up to date, there's no telling if your application actually works with the latest versions of all dependencies. Developers should deliberately upgrade and test to make sure there were no backwards-incompatible modifications in newer dependency library versions.
setup.py
There is another type of dependency specification for Python libraries known as setup.py. Setup.py is a standard for distributing and installing Python libraries. If you're building a Python library, such as requests or underwear you must include setup.py so a dependency manager can correctly install both the library as well as additional dependencies for the library. There's still quite a bit of confusion in the Python community over the difference between requirements.txt and setup.py, so read this well written post for further clarification.
Application dependency resources
-
Jon Chu wrote a great introduction on virtualenv and pip basics.
-
A non-magical introduction to virtualenv and pip breaks down what problems these tools solve and how to use them.
-
Tools of the modern Python hacker contains detailed explanations of virtualenv, Fabric, and pip.
-
Occasionally arguments about using Python's dependency manager versus one of Linux's dependency managers comes up. This provides one perspective on that debate.
-
Open source trust scaling is a good piece for the Python community (and other communities) that is based on the left-pad NPM situation that broke many dependent packages in the Node.JS community.
-
This Stack Overflow question details how to set up a virtual environment for Python development.
-
Another Stack Overflow page answers how to set environment variables when using virtualenv.
-
Tips for using pip + virtualenv + virtualenvwrapper shows how to use shell aliases and postactivate virtualenvwrapper hooks to make life easier when using these tools.
-
Major speed improvements were made in pip 7 over previous versions. Read this article about the differences and be sure to upgrade.
-
How to submit a package to PyPI is a short and sweet introduction that'll help you quickly get your first package on PyPI.
Open source app dependency projects
-
Autoenv is a tool for activating environment variables stored in a
.envfile in your projects' home directories. Environment variables aren't managed by virtualenv and although virtualenvwrapper has some hooks for handling them, it's often easiest to use a shell script or.envfile to set them in a development environment. -
Pipreqs searches through a project for dependencies based on imports. It then generates a
requirements.txtfile based on the libraries necessary to run those dependencies. Note though that while this could come in handy with a legacy project, the version numbers for those libraries will not be generated with the output.
Application dependencies learning checklist
-
Ensure the libraries your web application depends on are all captured in a requirement.txt file with pegged versions.
-
An easy way to capture currently installed dependencies is with the
pip freezecommand. -
Create a fresh virtualenv and install the dependencies from your
requirements.txtfile by using thepip install -r requirements.txtcommand. -
Check that your application runs properly with the fresh virtualenv and only the installed dependencies from the
requirements.txtfile.
What's next after installing app dependencies?

Searching for a complete, step-by-step deployment walkthrough? Learn more about The Full Stack Python Guide to Deployments book.
Email Updates
Application Dependencies
Need more detailed tutorials than you see here? Learn more about The Full Stack Python Guide to Deployments book.